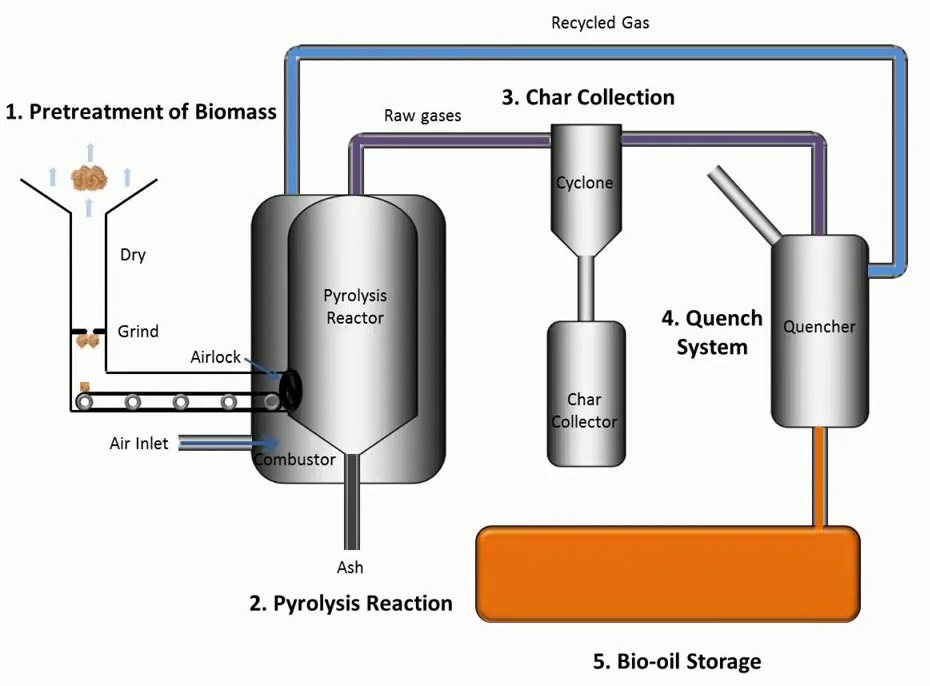
There are several different types of pyrolysis, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
One common type of pyrolysis is slow pyrolysis, which involves the breakdown of organic materials at relatively low temperatures (around 400-600 degrees Celsius) over a period of several hours. Biochar is a carbon-rich material that can improve soil fertility and increase crop yields using this pyrolysis process.
Another type of pyrolysis is fast pyrolysis, which involves the breakdown of organic materials at higher temperatures (around 500-700 degrees Celsius) over a shorter period of time (typically a few minutes). This type of pyrolysis is commonly used for the production of bio-oil, a liquid byproduct that can be further refined into a variety of chemicals and fuels.
Another form of pyrolysis is called wet pyrolysis, which involves the breakdown of organic materials in the presence of water. This type of pyrolysis can be used to produce hydrogen gas, which can be used as a clean-burning fuel for power generation. Wet pyrolysis is also commonly used for the synthesis of bioethanol and biodiesel.
Finally, there is a type of pyrolysis called gasification, which involves the breakdown of organic materials in the presence of oxygen. This process produces a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas, known as syngas, which can be used as a clean-burning fuel for power generation. The gasification process is also used to create chemicals such as methanol and acetic acid.
In conclusion, there are several different types of pyrolysis, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. By understanding the different types of pyrolysis, we can better utilize this process to convert waste materials into useful products and create a more sustainable future